There are roughly 4.3 billion IP addresses and we are out of IP addresses, do you know why? This is mainly because of the inventors of the internet. They mismanaged our IP address base which I will discuss below. We can't really blame it on them though because at that time they didn't realize that the Internet would become such a big deal and we would be assigning IP addresses to so many devices! Now, this is a serious problem because devices need the IP address to communicate. In this article, I will explain how the founders of the internet mismanaged and mishandled the IP addresses and then how Private IP addresses and NAT came to the rescue.
How the IP addresses were mismanaged?
The inventors of the internet mismanaged the IP addresses in the following ways-They put them into what are called classes A, B, C, D,&E.
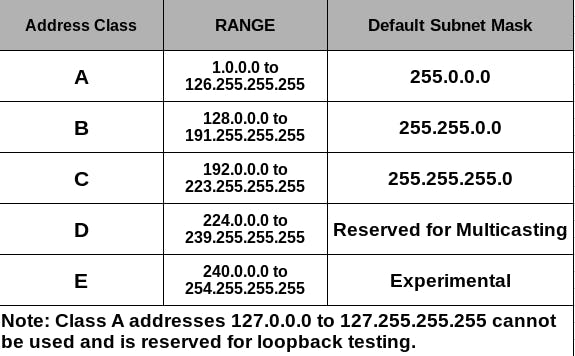
The problem with this arrangement is that there are large groups of IP addresses that we can't use. For example, class A addresses have over 16 million IP addresses in one network. Now, this class is only reserved for government entities or big companies and so we can't use this class. Also, having only one network and 16 million hosts or IP addresses can lead to a situation known as IP address exhaustion. This occurs when there are not enough IP addresses available to accommodate all of the hosts on a network. This can cause problems with network connectivity and performance, as hosts may not be able to communicate with each other or access resources on the network.
In the class B addresses, we have got fewer IP addresses i.e around 65,000 IP addresses but the flip side is we got more networks this time i.e around 16,000 networks. This class is again used by enterprises and organizations.
Now moving on down the line, we got class c, which will look most familiar to you right? Cuz it contains your home network. This was the best plan ever and they should have done this with every single network because here we got around 2 million networks and 254 hosts.
As for class D & class E, one is reserved for multicasting and the other is locked in for experimental purposes. Hence, these classes can't be used as well.
These were the reasons why we are out of IP addresses but don't worry because this problem of lack of IP addresses was solved with Private IP addresses and NAT very soon!
Private vs Public IP addresses
So far we have discussed about public IP addresses but you may be wondering what on earth is a public IP address?.... Well Public IP addresses are IP addresses that are used to communicate over the internet. They are assigned to devices, such as computers and servers, that connect to the internet and can be accessed over the internet from anywhere in the world. Basically, these are the IP addresses that we have been discussing about till now. Public IP addresses are unique and no one can have the same Public IP addresses.
Now, let's talk about Private IP addresses... You are aware that Public IP addresses are unique and it's impossible to have the same Public address but you may also be thinking that how on earth everyone in this world with so many devices can have a unique IP address since we are already running out of IP addresses? Well, that's where the climax begins!!
This is when the Private IP addresses were introduced. What they actually did was they took a few chunks out of our Public IP address ranges and made them private. Yes, that's legit what they did. Pretty bizarre right? They did an IP address transplant from each of the classes A, B,&C and made it private. The Private IP addresses are not unique by nature and this is exactly what solves the problem! If they are not unique then we can all share the same IP address and our problem will be solved...but hold on, it's too early to celebrate. There is one major problem with this and that is, these Private IP addresses will not connect you to the internet!! That's the big difference between Public & Private IP addresses. Private IP addresses are not publically routable on the internet. To solve this pesky internet problem we got introduced to the magical thing called NAT and this changed the game completely.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
So what exactly is NAT and what it does? Let's learn it through an example.
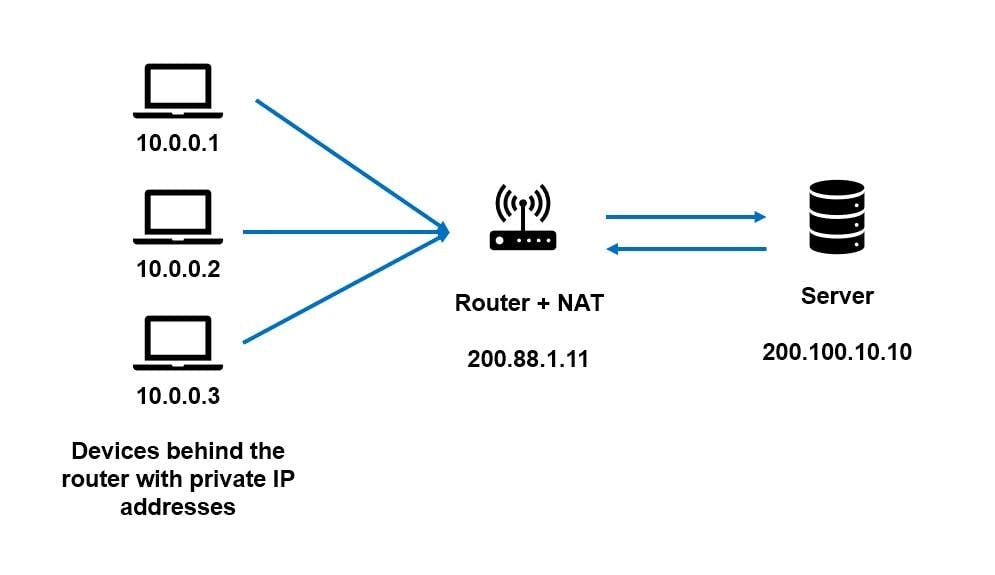
In your home network, you have got a lot of devices and it will be impossible to assign a public IP address to each of these devices because there is not enough for everyone. So instead we have our router to assign private IP addresses to each of the devices. Now let's say you wanted to download or watch anime at animepahe.ru which has a public IP address and it's out of your home network. How is your device going to communicate with servers of animepahe with a private IP address because private IP addresses can't connect to the internet, remember? So here comes your ISP(Internet Service Provider). You ask the ISP to connect your home to the internet, and ISP then provides 1 Public IP address to your router. Now you may be thinking that how 1 Public IP address is going to be enough to connect so many of your devices to the internet? I will tell you that with NAT it's more than enough. So what NAT will do (btw NAT is being performed by your router, she does it all, doesn't she?) is whenever any of your device wants to communicate with the servers of aniemepahe with its private IP address she will automatically translate that private IP address into the public address and enable communication between them. So every device in your network will have the same public address as the router and that saves everything. This literally saved the internet and it's how nearly every network you can think of works. Isn't this cool?
Some bad news😥...
Now I have got some bad news... even with the Private IP addresses and using NAT it didn't solve our problem, because we still did run out of IPv4 addresses (IPv4 is the IP address we have been talking about till now, it is the typical 4 number separated by 3 dots). So up came this IPv6 address which did solve our problem for the time being. We will discuss more about this in some other article.
Winding-up
In this article, we discussed how the Internet was going to end but it got saved by the Private IP address and NAT for the time being. In the coming articles, we will discuss about that mysterious dude known as Mr. Subnet Mask and what really is Subnetting. Till then, thanks for reading.
